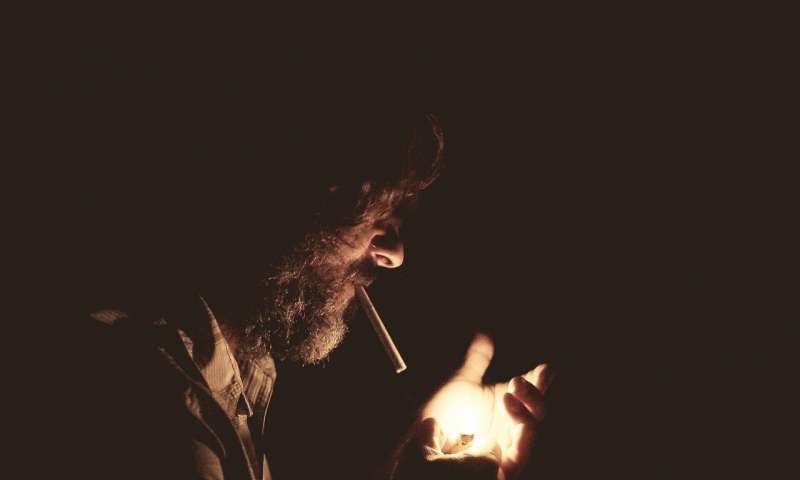
Smoking causes nearly one in five cancer cases and more than one in four cancer deaths each year in the U.K. Decades of policy action have steadily cut the U.K.”s smoking rates to one of the lowest in Europe. But with around one in seven people still smoking, tobacco continues to place an enormous cost on our society and our economy.
Last November, the U.K. Government published its vision to put “prevention at the heart of our nation’s health,” recognizing the importance of preventing cancer amongst other long-term health conditions. A new green paper, published yesterday, poses some new and old ways that the Government might deliver on this. And when it comes to tackling smoking, the plan to make England smoke free by 2030 is bold.
“We want to see smoking become a thing of the past, so it’s great to see the Government pledge to make this happen,” says Kruti Shrotri, Cancer Research U.K.”s policy manager.
But getting there can’t just be business as usual. If the Government really intends on achieving a smoke-free England by the end of the next decade, continued action on smoking is vital.
NHS and local government need support
“To make the England smoke free by 2030, we need to help people to quit smoking, particularly those who are hard to reach,” says Shrotri.
NHS England has promised that, by 2024, every hospital patient who smokes will be offered treatment to help them quit. But this isn’t enough. People also need to be offered treatment to quit by their GP. And local governments need funding to help them pay for vital services that are proven to bring smoking rates down.
“Smoking cessation services in local communities are being increasingly threatened,” says, Shrotri, referring to the impact of ongoing public health funding cuts across the country.
Slashed budgets have jeopardised vital public health services. And since 2015, the public health budget has fallen by £700 million. Funding for wider tobacco control measures and stop smoking services have been among the worst hit.
“We know stop smoking services, which offer smokers a combination of pharmacotherapy and behavioral support, are the most successful way to support smokers to stop,” says Shrotri. “However, ongoing cuts to public health funding have meant that just over half the local authorities in England have a specialist stop smoking service open to all smokers in the area.”
Reducing smoking rates will also help tackle health inequality. Right now, the gap in life expectancy between the richest and the poorest is widening. And because smoking rates are highest amongst the most vulnerable in society, tackling smoking is the single best thing we can do to improve that gap.
Possibility of a ‘polluter pays’ approach
Tobacco companies are responsible for the greatest and most enduring man-made public health epidemic in history, yet they continue to profit from a product that kills one in two people who use it. In its green paper, the Government recognizes that charging tobacco companies in France and the U.S. for the damage they cause has helped to fund some tobacco control efforts, suggesting that the U.K. may be open to a similar approach.
“These new Government proposals mention a charge on the tobacco industry,” says Shrotri. “This is something we and others have been trying to push since 2015, so we’re really pleased they’ve acknowledged it as part of a potential solution to plug the current funding gap for tobacco control.”
More than 7 in 10 adults in England said they’d support a fee on tobacco manufacturers that could fund stop smoking services and prevent young people from taking up smoking, according to a YouGov survey commissioned by Action on Smoking and Health (ASH).
“It’s a matter of fairness,” says Shrotri, “that the tobacco industry should pay for the damage to health that they’ve caused.”
Alongside this, the green paper also suggests that an insert carrying quitting advice could be included inside cigarette packs. Canada is the only country in the world that does this, and evidence suggests this could discourage young adult smokers from continuing to smoke.
What happens next?
This latest Government document is only a series of suggestions. The proposals are now out in the public domain and open for debate.
Organisations and companies with an interest in the proposed measures—whether they prioritize public health or not—are now free to weigh in and attempt to influence how these proposals are taken forward.